Chemical burns can happen in an instant, leaving the skin damaged and causing severe pain. These injuries often result from exposure to household cleaners, industrial chemicals, or accidents in laboratories. The burning sensation may not stop immediately, and in some cases, the damage continues to worsen if not treated quickly.
Surprisingly, chemical burns are responsible for thousands of emergency room visits each year, especially among those unaware of the correct first aid steps. Many individuals feel overwhelmed and unsure of how to react in such situations, which can delay proper care.
In this guide, we’ll explore how to handle chemical burns safely and effectively. You’ll learn the crucial first-aid measures that can minimize damage, reduce pain, and speed up recovery.
Why Should You Know This?
Chemical burns are not limited to laboratories. Plenty of household cleaning supplies can cause serious burns, and in certain countries acid attacks have become a common means of assault.
Household Chemicals to Be Cautious Around
Drain cleaner
Bleach and ammonia cleaners
Mold and mildew cleaners
Furniture polishes
Laundry Detergents
Toilet cleaners
Oven cleaners
Carpet cleaners
Window cleaners
Insect spray
Weed killer
Aerosol-based air fresheners And more
Types of Exposure
Chemicals can affect the body through inhalation, ingestion, and skin contact. Ingestion and inhalation are the most hazardous forms of exposure because they can easily cause organ damage. Skin contact is less hazardous because it is usually the easiest to treat and prevent.
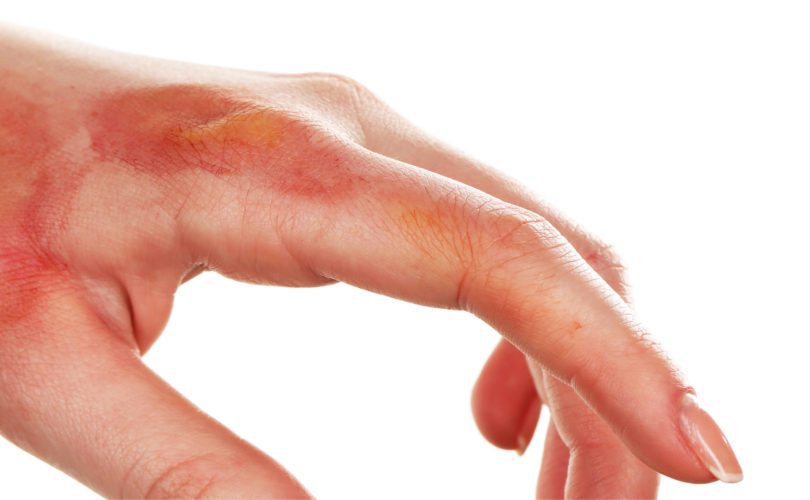
What Are the Symptoms of Chemical Burns?
- Redness, irritation, and pain at the site of contact
- Swelling and possible blistering in the affected area
- Skin peeling and discoloration (may turn white, black, or yellow depending on the chemical)
- Numbness or tingling, especially with strong acids or alkalis
- Eye irritation and vision problems if the chemical gets into the eyes
How to Treat Chemical Burns?
If you ingest or inhale the chemical, follow the directions on the container for proper procedures.
For solid chemicals, brush it off into a safe area where it will not harm anyone or anything else, then flush the area with water. If it is a metal compound, a mineral oil will be needed to remove the chemical.
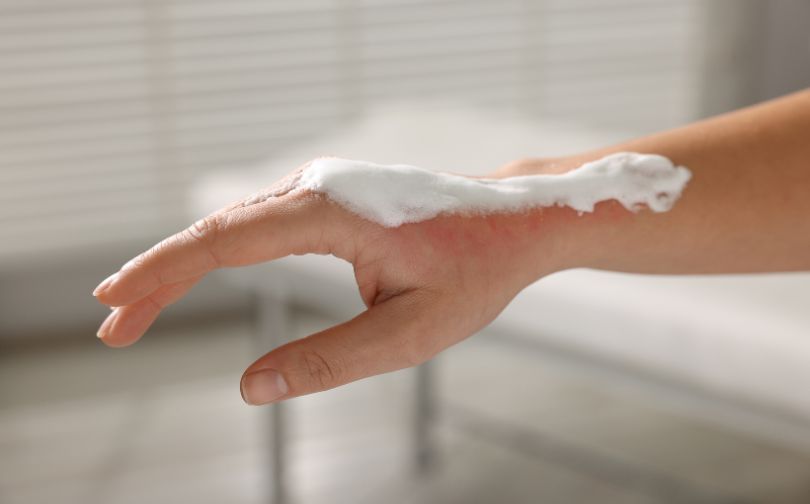
If it is skin contact with a liquid chemical run the affected area under a gentle to medium strength stream of cold water* for 20 minutes, or until any pain or discomfort stops. Always use cold water because warm and hot water will cause your pores to open, allowing the chemical to penetrate your skin faster. Do not rub the affected area while flushing.
*Do not flush carbolic or phenol with water, they wont mix with water. Flush the area with rubbing alcohol first, and then flush with water. Use a mild soap and water for sulfuric acid.
If the chemical gets on clothing, remove it immediately and rinse the affected areas.
Remove any jewelry as you rinse the area, unless the jewelry has fused to the skin.
If the chemical gets into your eyes, use an eyewash, eyewash station, or cold tap water.
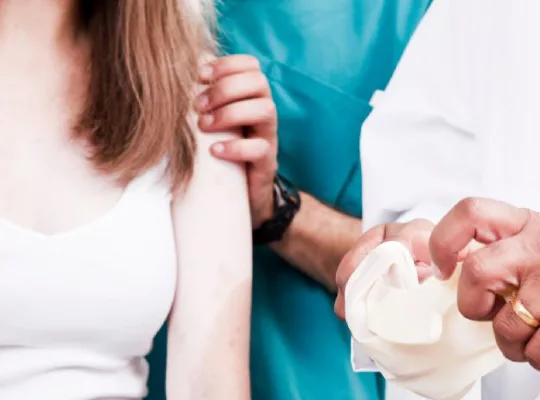
Once the area has been flushed, apply a non-adherent bandage, or gauze secured with medical tape. If the burning sensation returns, remove the covering and flush with water, or necessary material again. Seek medical help depending on the severity of the burn, and the chemical that caused the burn.
How to Prevent Chemical Burns?
The best way to prevent a chemical burn is to wear proper protection. Use rubber or nitrile gloves, eye protection, long sleeves, close toed shoes, an apron, especially lab aprons, are all great ways to protect yourself from chemicals. Always read the safety and hazard information for the chemical ahead of time. The faster you can react to a spill, the chance of a serious burn decreases.
Conclusion
Chemical burns can be dangerous, painful, and often worsen without quick and proper treatment. They commonly result from exposure to household cleaners and industrial chemicals, making awareness of prevention and response critical for safety.
Thousands of people visit emergency rooms every year for chemical burns, underscoring the need for understanding effective first-aid steps. Knowing how to treat these burns—such as flushing the affected area with cold water and using the correct type of cleanser—is essential for reducing pain and minimizing skin damage.
Prevention is equally important. Wearing gloves, eye protection, and other protective gear can help avoid exposure to harmful chemicals. By following these precautions and treatment steps, you can better protect yourself and others from the risks associated with chemical burns.
FAQs
Should I Call Emergency Services for a Chemical Burn?
Yes, call emergency services (911) if the burn is large, deep, or affects sensitive areas like the face, eyes, hands, feet, groin, or joints. Immediate care is crucial if there’s difficulty breathing, dizziness, or if the burn area covers more than three inches in diameter.
What Should I Avoid Doing When Treating a Chemical Burn?
Avoid applying creams, ointments, butter, or oils to the burn, as these can worsen the injury. Do not use ice or cold water, as this can cause additional damage. Also, avoid trying to neutralize the chemical with another substance like vinegar or baking soda.
How Do I Treat a Chemical Burn in the Eye?
Flush the affected eye with large amounts of water for at least 20 minutes, ideally in a shower or at an eyewash station. Seek emergency medical attention immediately after rinsing, as prompt professional care is essential for preventing serious eye damage.
What Should I Do if Dry Chemicals Are Involved?
For dry chemical burns, gently brush off any remaining particles before rinsing with water. Avoid spreading the chemical to other body areas during this process to prevent additional irritation or burns.