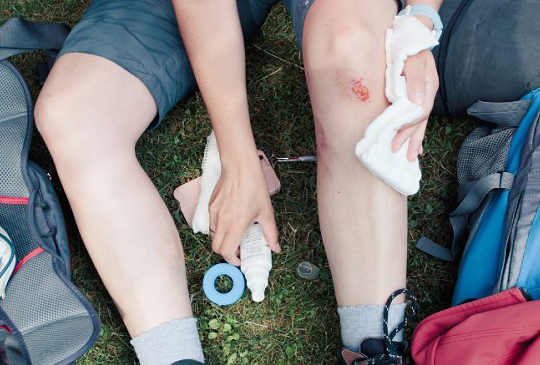
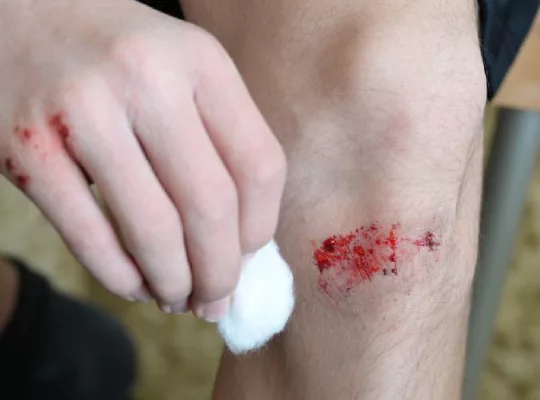
Open wounds can occur as a result of accidents, injuries, or medical procedures. They are injuries where the skin is broken, and the underlying tissues are exposed to the environment, increasing the risk of infection.
There are different types of open wounds, including puncture wounds, abrasions, lacerations, and avulsions, each with its unique characteristics and severity.
Understanding the different types of open wounds and their specific care requirements can help prevent complications and promote effective healing.
In this article, we will explore the various types of open wounds, their causes, symptoms, and proper care techniques. We will also provide essential tips on when to seek medical attention for more severe cases.
Types Of Open Wounds
Here is a list of the different types of open wounds, along with long summaries explaining their characteristics, causes, symptoms, and treatment options:
Puncture Wounds
Puncture wounds are deep wounds caused by sharp, pointed objects that penetrate the skin and underlying tissues. These wounds are narrow, often difficult to clean, and can result in significant damage to the internal organs or tissues.
Common causes of puncture wounds include stepping on nails, animal bites, or being impaled by a sharp object. Symptoms may include bleeding, pain, swelling, and redness around the wound.
Treatment typically involves cleaning the wound, applying pressure to stop the bleeding, and administering antibiotics to prevent infection. In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to repair damaged tissues.
Abrasions
Abrasions, also known as scrapes, occur when the skin is rubbed or scraped against a rough surface, resulting in the removal of the top layer of skin. They are often shallow wounds and can be painful and prone to infection.
Common causes of abrasions include falls, sports injuries, and road rash. Symptoms may include bleeding, pain, and redness around the wound. Treatment typically involves cleaning the wound, applying antibiotic ointment, and covering it with a sterile dressing to promote healing.
Lacerations
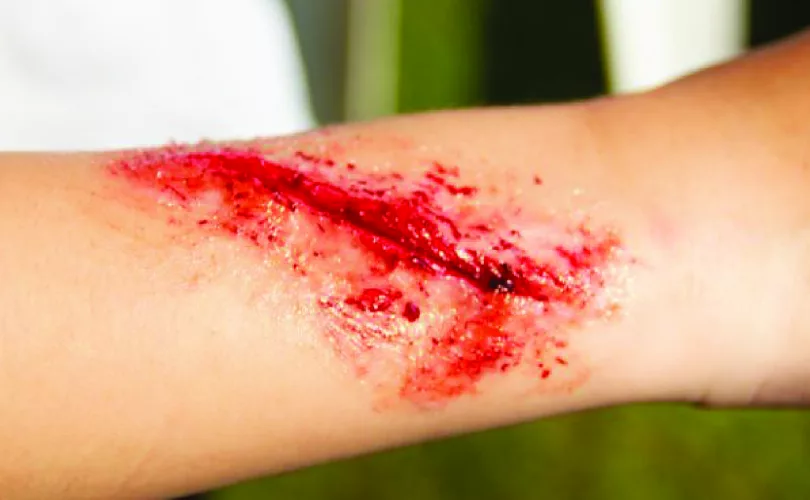
Lacerations are deep cuts or tears in the skin that may extend into the underlying tissues. They can be caused by sharp objects such as knives, broken glass, or metal. Symptoms may include bleeding, pain, swelling, and redness around the wound.
Treatment typically involves cleaning the wound, stopping the bleeding, and stitching the wound closed to promote healing. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to repair damaged tissues.
Avulsions
Avulsions occur when a portion of the skin and underlying tissues is torn away from the body. These wounds are often severe and can result in significant blood loss and damage to surrounding tissues.
Common causes of avulsions include severe accidents, animal attacks, and surgical procedures. Symptoms may include bleeding, pain, swelling, and redness around the wound.
Treatment typically involves cleaning the wound, stopping the bleeding, and performing surgery to repair the damaged tissues.
Incisions
Incisions are clean, straight cuts made by a sharp object, such as a surgical scalpel. These wounds are often made intentionally during surgical procedures and are carefully closed with stitches or staples to promote healing.
Symptoms may include bleeding, pain, and redness around the wound. Treatment typically involves cleaning the wound, stopping the bleeding, and closing the wound with sutures or staples.
Gunshot Wounds
Gunshot wounds are caused by bullets that penetrate the skin and underlying tissues, resulting in significant damage to the internal organs and tissues. These wounds can be severe and life-threatening and require immediate medical attention.
Symptoms may include bleeding, pain, swelling, and redness around the wound. Treatment typically involves stabilizing the patient, stopping the bleeding, and performing surgery to repair the damaged tissues.
Open wounds are a common occurrence and can vary in severity and cause. Understanding the different types of open wounds and their specific care requirements is crucial for effective treatment and promoting proper healing.
If you experience an open wound, seek medical attention promptly to prevent complications and ensure the best possible outcome.
Treatment Stages For Open Wounds
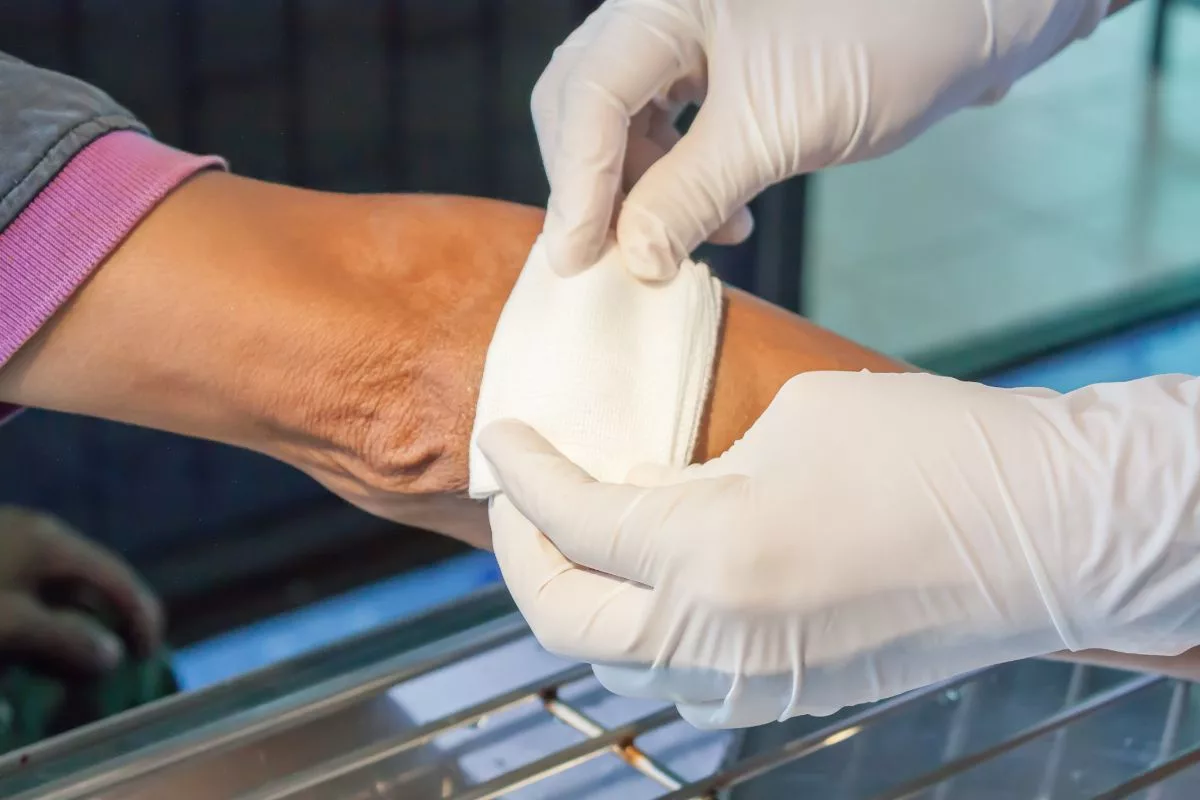
The treatment for open wounds depends on the type, severity, and cause of the injury. However, there are general stages of treatment that can be applied to most open wounds. Here are the four main stages of treatment for open wounds:
Stop The Bleeding
The first step in treating an open wound is to stop the bleeding. Apply pressure directly to the wound with a clean cloth or sterile gauze until the bleeding stops.
Elevating the affected limb or area above the heart level can also help to slow down the bleeding. If the wound is severe and bleeding cannot be controlled, seek medical attention immediately.
Clean The Wound
Once the bleeding has stopped, clean the wound thoroughly to remove any dirt, debris, or bacteria that may have entered. Use clean water or saline solution to rinse the wound gently.
Avoid using alcohol, hydrogen peroxide, or iodine, as they can delay healing and damage healthy tissue. Pat the wound dry with a clean cloth.
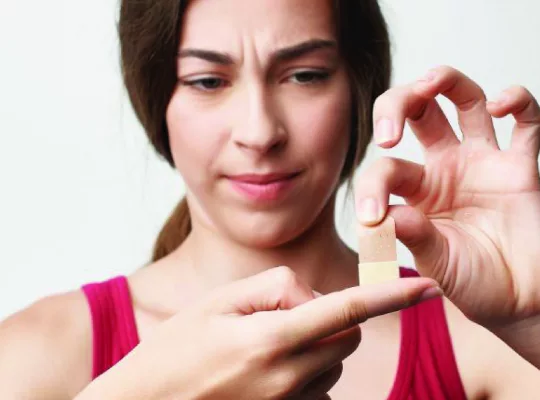
Apply An Appropriate Dressing
After cleaning the wound, apply an appropriate dressing to cover and protect the wound. The dressing should be sterile, non-stick, and breathable. It should also be changed regularly to prevent infection and promote healing.
Depending on the type and severity of the wound, your healthcare provider may recommend a specific type of dressing, such as an antibiotic ointment or a hydrogel.
Monitor The Wound
Monitor the wound for signs of infection, such as increased pain, redness, swelling, or drainage. Change the dressing regularly, and keep the wound clean and dry. If the wound does not heal within a reasonable time or shows signs of infection, seek medical attention immediately.
In addition to these general stages, specific treatment may be necessary depending on the type and severity of the wound. For example, puncture wounds may require antibiotics to prevent infection, while lacerations may require stitches or staples to close the wound.
Seek medical attention if you are unsure about how to treat an open wound or if the wound is severe or shows signs of infection.
Preventing Infection
Preventing infection in open wounds is crucial for proper healing and minimizing the risk of complications.
The key steps to prevent infection in open wounds include promptly cleaning the wound, using appropriate dressings that are sterile, non-stick, and breathable, changing the dressing regularly, and avoiding touching the wound with dirty hands.
It is also important to monitor the wound for signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, or drainage, and to seek medical attention if any signs of infection appear.
Final Thoughts
Open wounds can be caused by various types of injuries, including abrasions, lacerations, punctures, and avulsions. Each type of open wound requires a different approach to treatment, and the severity of the wound determines the necessary level of care.
It is crucial to stop the bleeding, clean the wound, apply appropriate dressing, and monitor the wound for signs of infection to promote proper healing and minimize the risk of complications.
By understanding the different types of open wounds and following appropriate treatment protocols, individuals can help to prevent infection and promote faster healing. If you have any concerns about an open wound or are unsure about how to treat it, seek medical attention immediately.