A common issue people face is that hives can vary in size and location, making it difficult to pinpoint the cause or find a reliable remedy. According to the American Academy of Dermatology, hives affect about 20% of people at some point in their lives, which highlights how widespread the problem is.
What Are Hives?
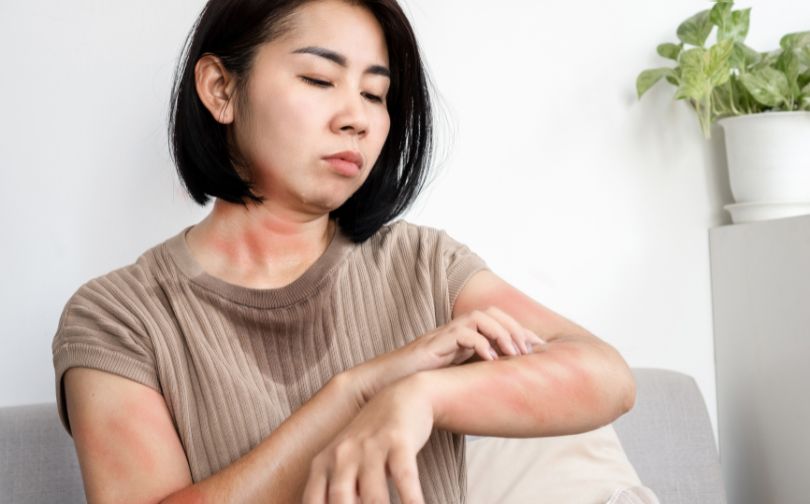
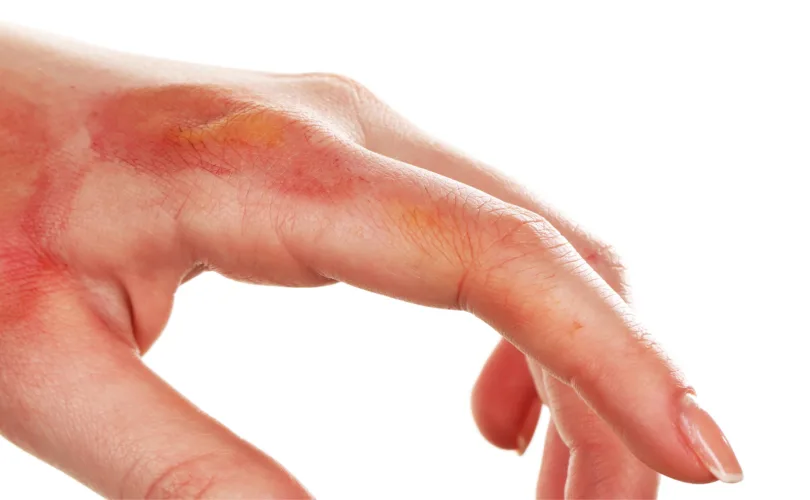
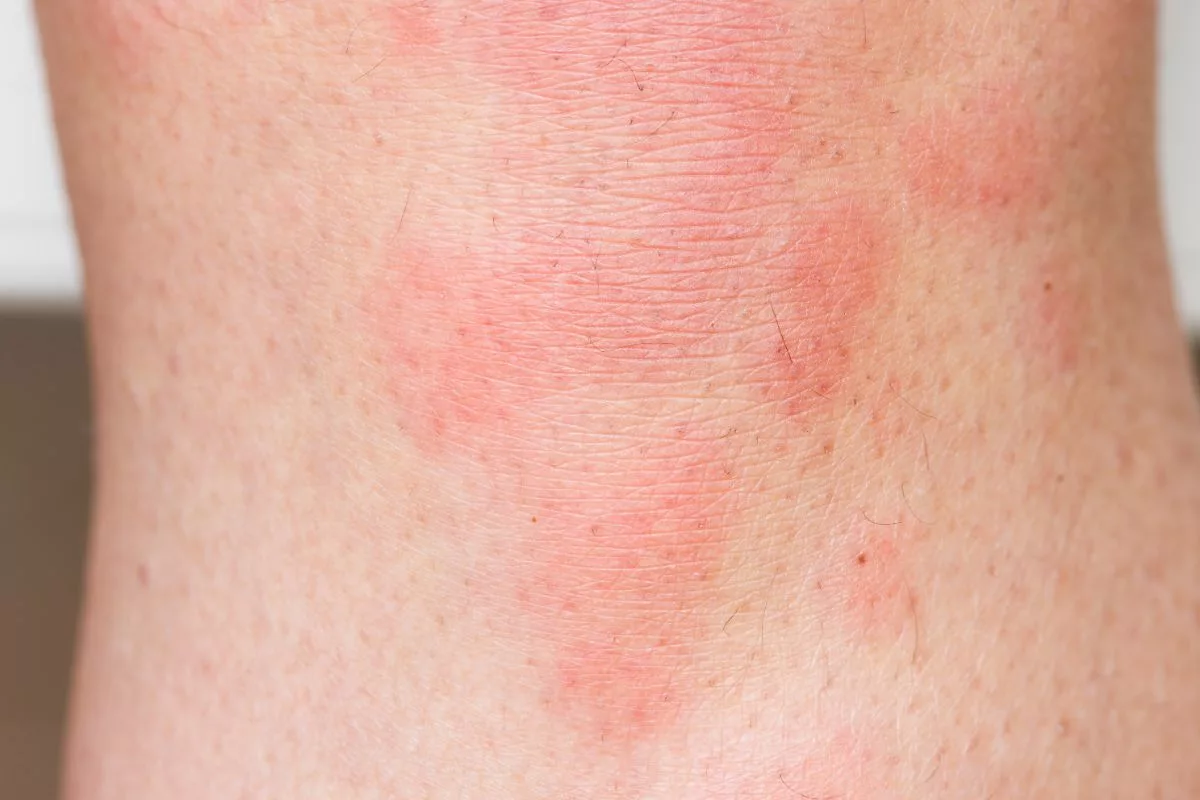
Hives, also known as urticaria, is a common skin condition characterized by itchy and swollen bumps on the skin.
Hives can appear anywhere on the body and range in size from small dots to large patches.
They can be round or shaped like rings and may be red or flesh-colored. Hives are typically caused by an allergic reaction to something, such as food, medication, or insect bites.
Other common triggers of hives include stress, heat, cold, and pressure on the skin.
In most cases, hives are harmless and disappear on their own within a few hours or days.
However, in some cases, hives can be a symptom of a more serious allergic reaction that requires medical attention.
Chronic hives, which last for six weeks or more, can also be a sign of an underlying medical condition.
The symptoms of hives can be uncomfortable and affect your quality of life. They can cause itching, swelling, and a burning or stinging sensation on the skin.
If you’re experiencing hives, it’s important to identify the cause and take steps to prevent future outbreaks.
There are several treatment options available for hives, including over-the-counter medications, home remedies, and lifestyle changes.
Over The Counter Medications
Over-the-counter (OTC) medications are a common treatment option for hives.
These medications can help relieve itching, swelling, and other symptoms associated with hives. Here are some OTC medications commonly used for hives:
- Antihistamines: These medications block the release of histamine, a chemical that causes itching and swelling. Common OTC antihistamines include diphenhydramine, loratadine, and cetirizine.
- Anti-inflammatory creams: OTC creams containing corticosteroids can help reduce swelling and itching associated with hives. Examples of corticosteroid creams include hydrocortisone and triamcinolone.
- Pain relief: Over-the-counter medications like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can relieve the pain and discomfort associated with hives.
When using OTC medications for hives, it’s important to follow the instructions carefully and consult with a healthcare provider if you have any questions or concerns.
In some cases, OTC medications may not be effective, and prescription medications may be necessary. It’s also important to identify and avoid triggers that may be causing hives, as this can help prevent future outbreaks.
Home Remedies
In addition to OTC medications, there are many home remedies available that could help alleviate the symptoms of hives. Here are some commonly used home remedies for hives:
- Cold compress: Applying a cold compress to the area could help reduce itching and swelling. Simply wrap a few ice cubes in a towel and apply to the hives for 10-15 minutes at a time.
- Oatmeal bath: Taking a bath with colloidal oatmeal can help soothe irritated skin and relieve itching. Colloidal oatmeal is available at most drug stores.
- Aloe vera: Using aloe vera gel could help reduce inflammation and calm the skin.
- Baking soda: Adding baking soda to a warm bath can help relieve itching and soothe the skin.
- Apple cider vinegar: Trying a solution of apple cider vinegar and water may help reduce itching and inflammation.
It’s important to note that while home remedies can provide relief for hives, they may not be effective for everyone.
If you experience severe symptoms or your hives do not improve with home remedies, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional.
Additionally, it’s important to identify and avoid triggers that may be causing your hives to prevent future outbreaks.
Lifestyle Changes
Making certain lifestyle changes can help prevent or reduce the frequency and severity of hives outbreaks. Here are some lifestyle changes that may be helpful for managing hives:
- Avoid triggers: Identify and avoid triggers that may be causing your hives outbreaks. Common triggers include certain foods, medications, and environmental factors such as heat, cold, or pressure on the skin.
- Wear loose-fitting clothing: Tight-fitting clothing can irritate the skin and trigger hives outbreaks. Wearing loose-fitting clothing made of breathable materials such as cotton can help reduce irritation.
- Manage stress: Stress can weaken the immune system and trigger hives outbreaks. Engaging in stress-reducing activities such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises may be helpful.
- Maintain good hygiene: Keeping your skin clean and well-moisturized can help prevent hives outbreaks. Use mild, fragrance-free soap and moisturizer.
- Stay hydrated: Drinking plenty of water can help keep your skin healthy and hydrated, which can reduce the frequency and severity of hives outbreaks.
- Quit smoking: Smoking can weaken the immune system and trigger hives outbreaks. Quitting smoking may be helpful for managing hives.
It’s important to note that lifestyle changes may not be effective for everyone with hives, and medical treatment may be necessary.
If you experience severe symptoms or your hives do not improve with lifestyle changes, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional.
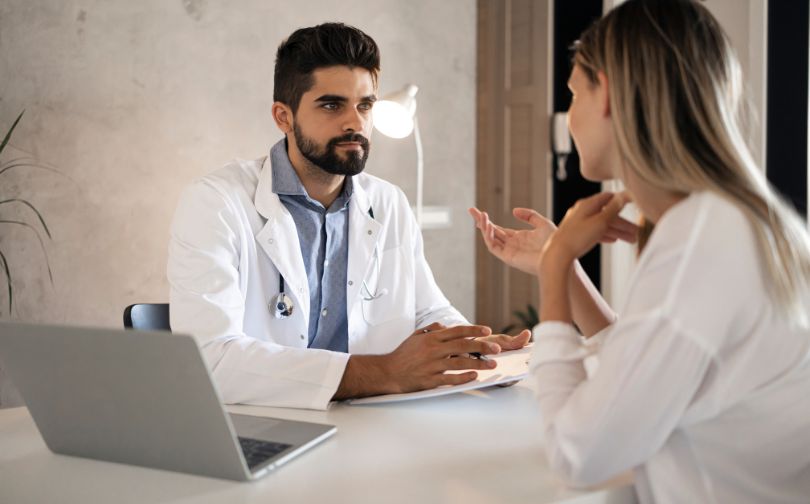
When Should You See A Doctor For Hives?
In most cases, hives are harmless and will go away on their own within a few hours or days.
However, there are certain situations where you should see a doctor for hives. Here are some situations where medical attention may be necessary:
- Severe symptoms: If you experience severe symptoms such as difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat, or dizziness, consult a healthcare professional immediately as these can be signs of a serious allergic reaction.
- Chronic hives: If your hives last for more than six weeks, it may be a sign of an underlying medical condition such as an autoimmune disorder. Your doctor may recommend further testing or refer you to a specialist.
- Recurrent outbreaks: If you experience recurrent outbreaks of hives, it’s important to see a doctor to identify and address the underlying cause.
- Hives accompanied by other symptoms: If your hives are accompanied by other symptoms such as fever, joint pain, or fatigue, it may be a sign of an underlying medical condition.
- Hives in children: If your child has hives, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional as children may have a more severe reaction to hives than adults.
If you are unsure whether or not to consult a healthcare professional for your hives, it’s always best to err on the side of caution and consult with a healthcare provider.
They can help you determine the best course of action for managing your hives.
Final Thoughts
Hives can be a bothersome and uncomfortable condition, but there are a variety of treatment options available to help alleviate the symptoms.
Over-the-counter medications such as antihistamines and topical creams can be effective in treating mild cases of hives, while home remedies and lifestyle changes can also provide relief.
However, if you experience severe symptoms, chronic hives, or recurrent outbreaks, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional to identify and address the underlying cause.
With the right treatment approach, most people with hives can find relief from their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
FAQs
Can Lifestyle Changes Help Manage Hives?
Yes, lifestyle changes such as avoiding known triggers, wearing loose clothing, and applying cold compresses can help manage hives. Stress reduction techniques like meditation or yoga may also be beneficial in reducing flare-ups, contributing to overall management of symptoms. Consult a doctor for personalized advice.
How Do Antihistamines Work in Treating Hives?
Antihistamines treat hives by blocking the action of histamine, a chemical that your body releases during allergic reactions. This prevents the itching, redness, and swelling associated with hives. Over-the-counter and prescription options are available, with varying dosages depending on the severity of symptoms.
Are There Any Side Effects of Antihistamines?
Some antihistamines can cause drowsiness, dry mouth, or dizziness. Non-drowsy formulations are available for daytime use. It’s important to follow dosage instructions and consult a healthcare provider, especially if you are taking other medications or have pre-existing conditions like high blood pressure.
Can Chronic Hives Be Cured?
Chronic hives are often managed rather than cured. Treatment typically involves long-term use of antihistamines and identifying potential triggers, such as foods or environmental factors. In some cases, advanced therapies like immunosuppressants or biologics may be necessary under a doctor’s supervision.